Graphite Note Ready-To-Use AI Models
Make impactful decisions with Graphite Note’s growing selection of no-code Machine Learning models for your every need.
Activating a trial gives you 14 days to kick the tires.
No card is required.
Enjoy click-to-connect AI models for a wide range of advanced analytics business needs
A predictive analytics solution for your every business question.
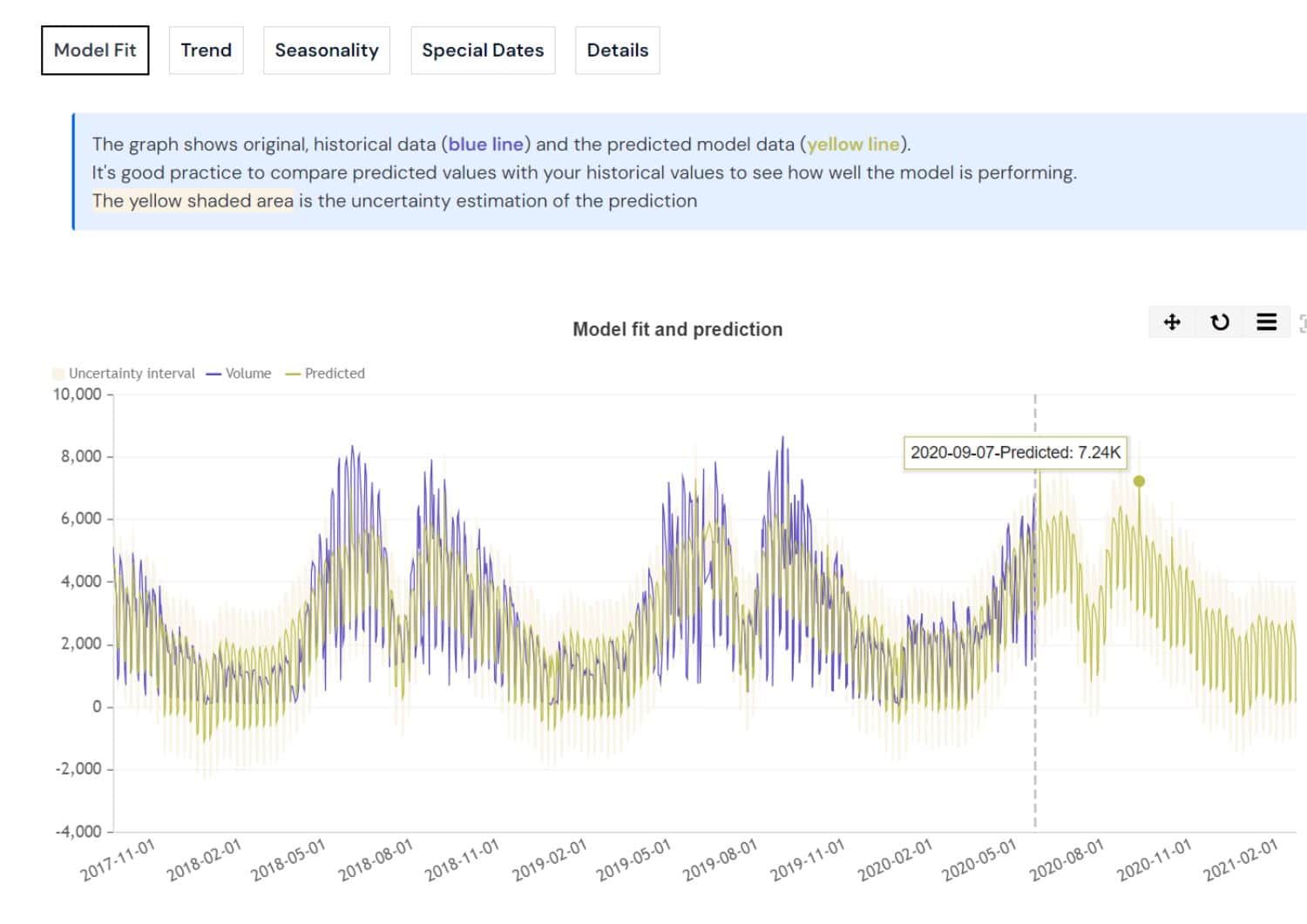
Time-series forecasting is looking at recorded data over time to forecast or predict what might happen in the next time period, under the assumption that future trends will be similar to historical trends.
- What revenue are we going to have 6 months from now?
- How much inventory should we stock tomorrow, or 30 days from now, to meet demands?
- How many customers will return next week or month?
- What is the effect of our product promotion and what can we expect from future promotions?
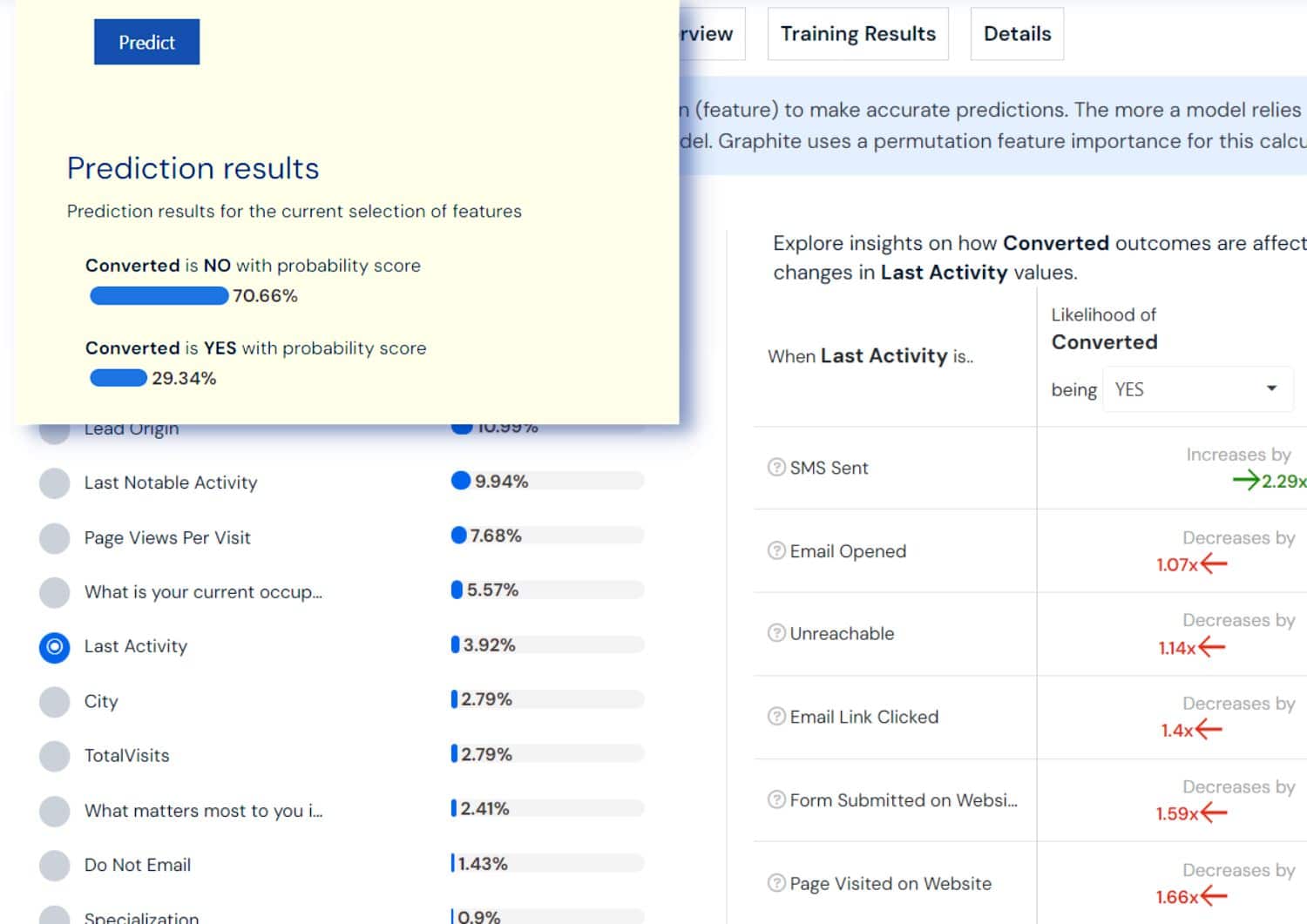
Binary Classification: This is about predicting one of two outcomes based on past data. It helps in deciding whether something will happen or not, like if a customer will make a purchase.
- Predict customer churn: Who stays and who leaves?
- Email campaign effectiveness: Which will be opened, and which ignored?
- Fraud detection in transactions: Legitimate or suspicious?
- Equipment failure predictions: Operate or repair?
- Marketing campaign success: Convert or not?
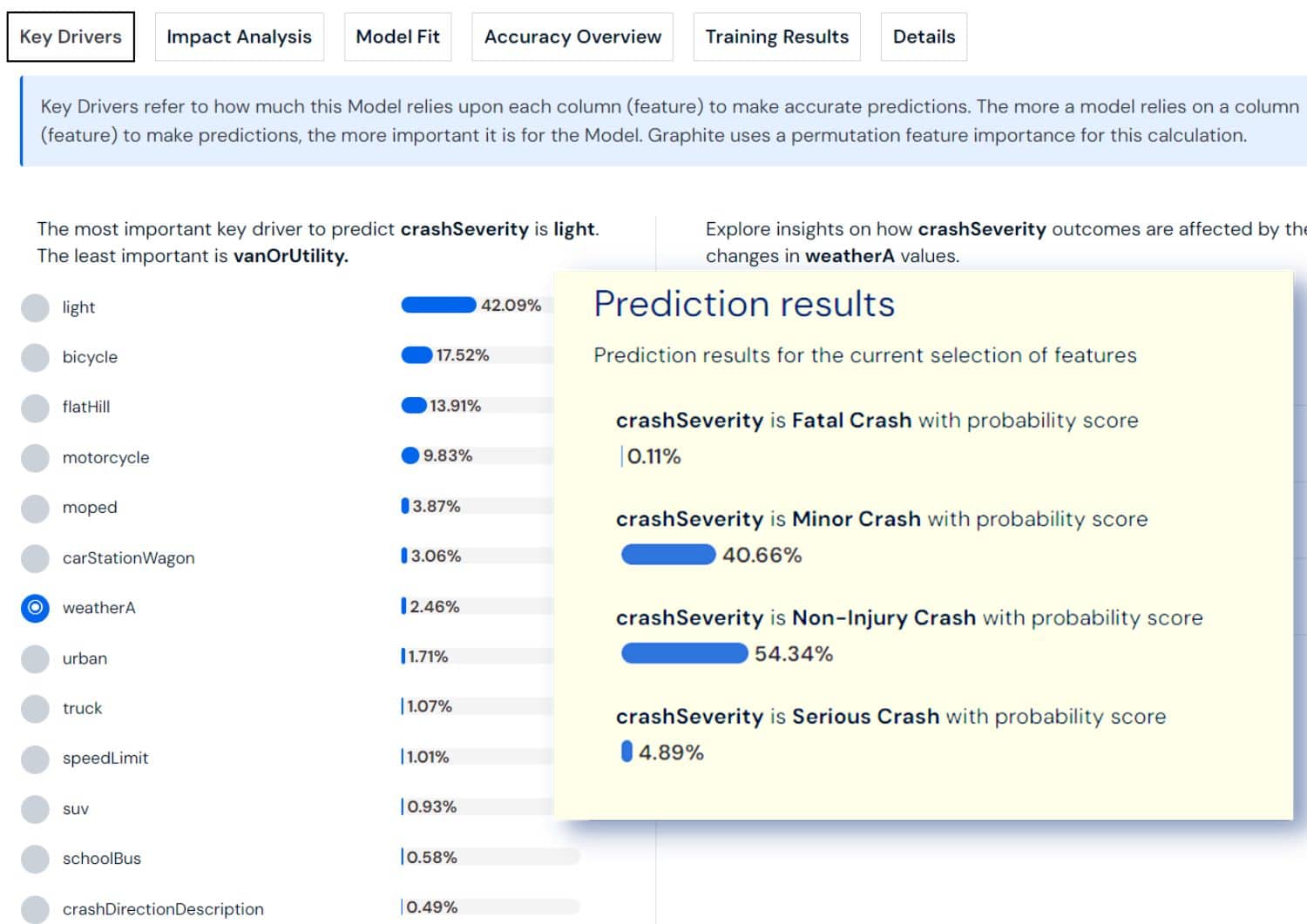
Multiclass Classification: This approach extends beyond binary options, predicting outcomes among three or more categories based on historical data. It's about identifying which specific group an event or item belongs to.
- Predict customer segment: Which category does each customer fit into?
- Content recommendation: What type of content will a user prefer?
- Product categorization: Which category does each product belong to?
- Disease diagnosis: What type of condition does a patient have?
- Sentiment analysis: Is the feedback positive, negative, or neutral?
Regression: This method predicts continuous outcomes based on past data. It’s about estimating numerical values, like sales figures or temperatures, rather than choosing between categories.
- Sales forecasting: How much will be sold next quarter?
- Price prediction: What will be the future price of a product or service?
- Demand estimation: How many customers will want this product?
- Energy consumption: How much energy will a building use next month?
- Website traffic: How many visitors will come to the website next week?
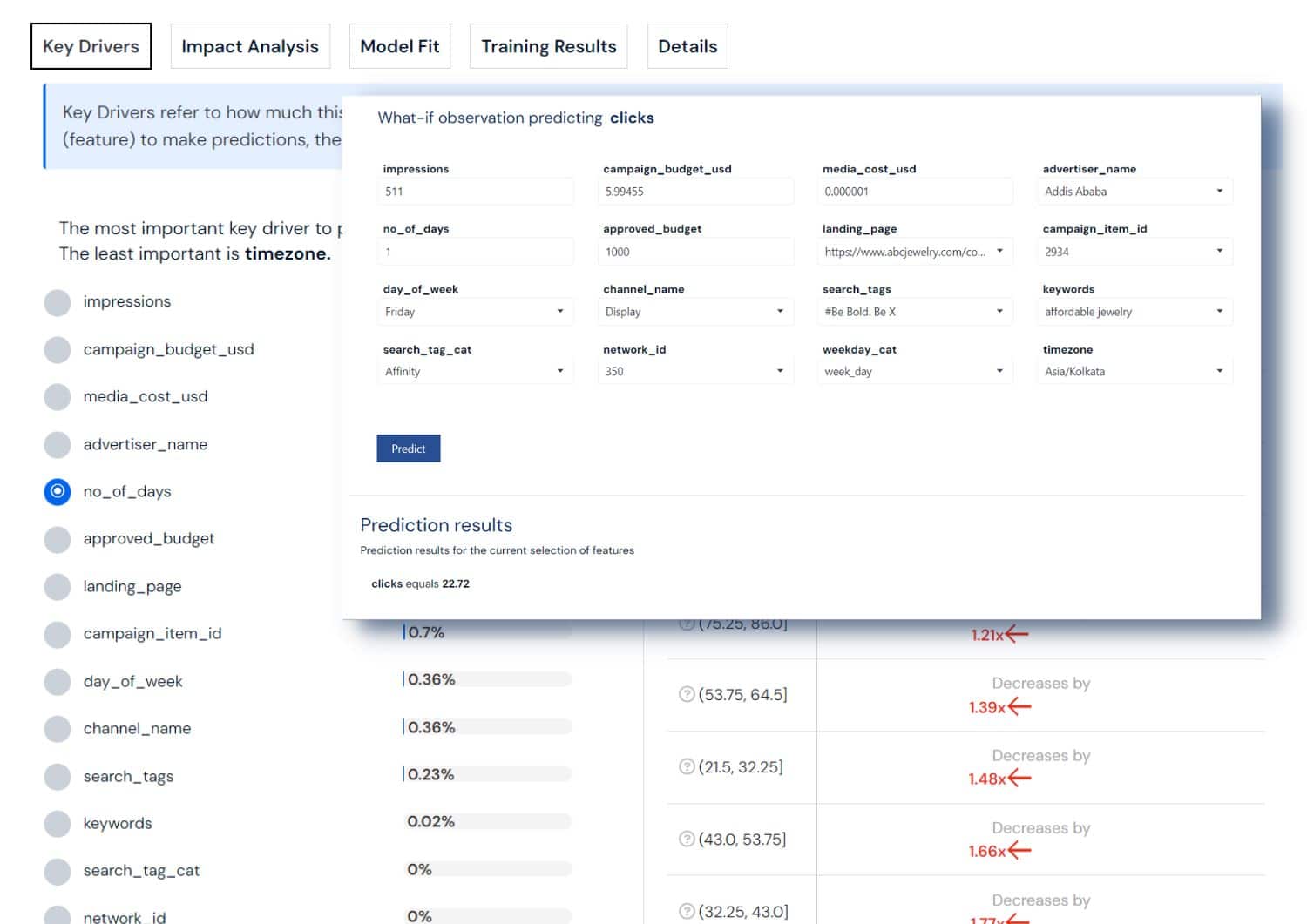
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Prediction: This method, based on "buy till you die" statistical distribution, estimates the total value a customer will bring to a business over the entirety of their relationship. It's crucial for understanding and maximizing the long-term value of customer relationships.
- Value forecasting: What is the projected value of each customer?
- Relationship duration: How long will a customer stay engaged with the brand?
- Purchase frequency: How often will a customer make a purchase?
- Profit optimization: Which customers are most profitable to focus on?
- Retention strategies: What actions can increase customer loyalty and value?
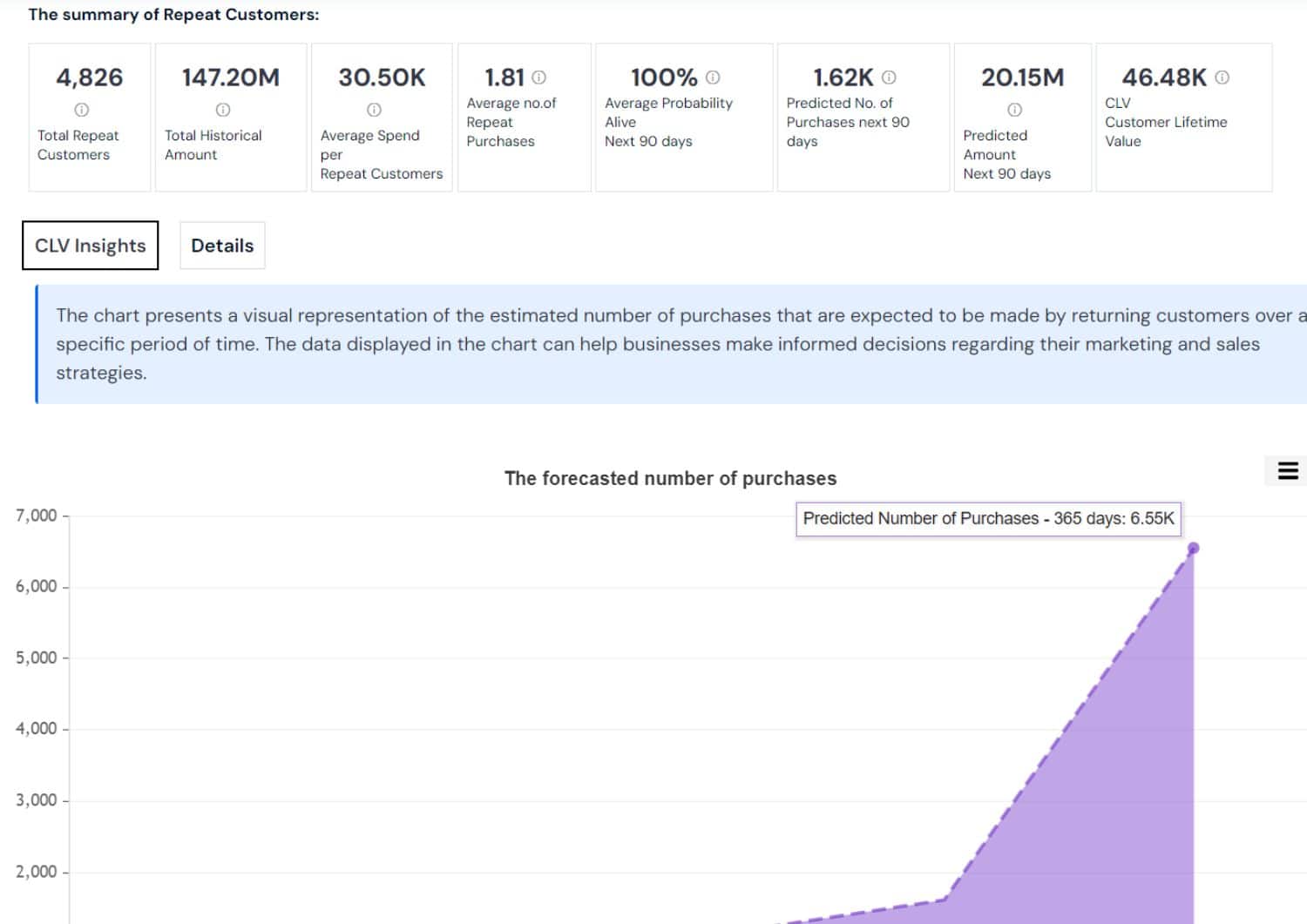
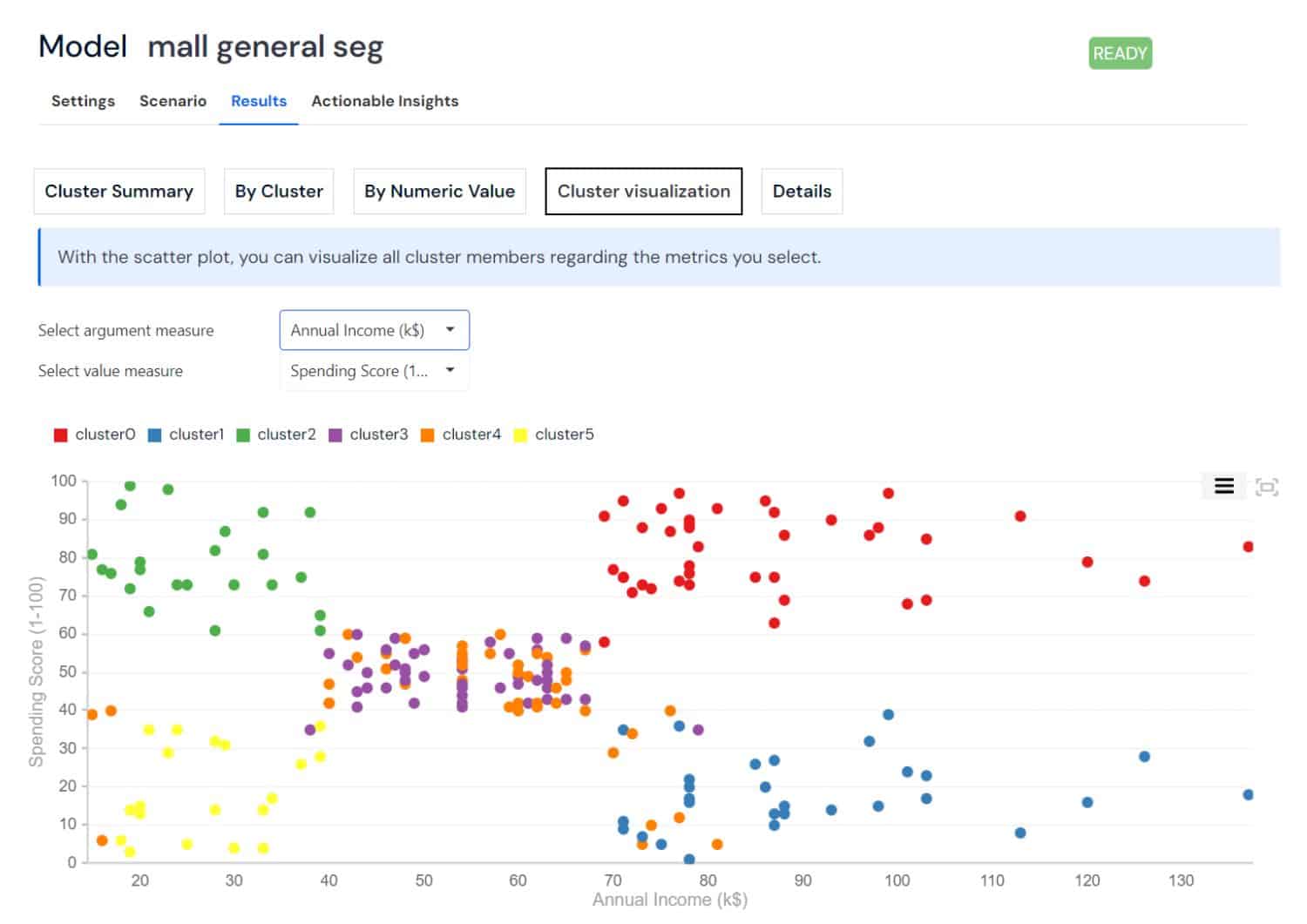
General Segmentation (Clustering): This technique groups similar data points together based on their characteristics, without predefined categories. It's used to discover natural groupings within data, like customer segments or product types.
- Customer behavior: Which customers have similar shopping habits?
- Market segmentation: How can markets be divided based on consumer preferences?
- Product categorization: What products appeal to similar customer groups?
- Anomaly detection: Which data points do not fit into any group?
- Targeted marketing: How to tailor marketing strategies for each segment?
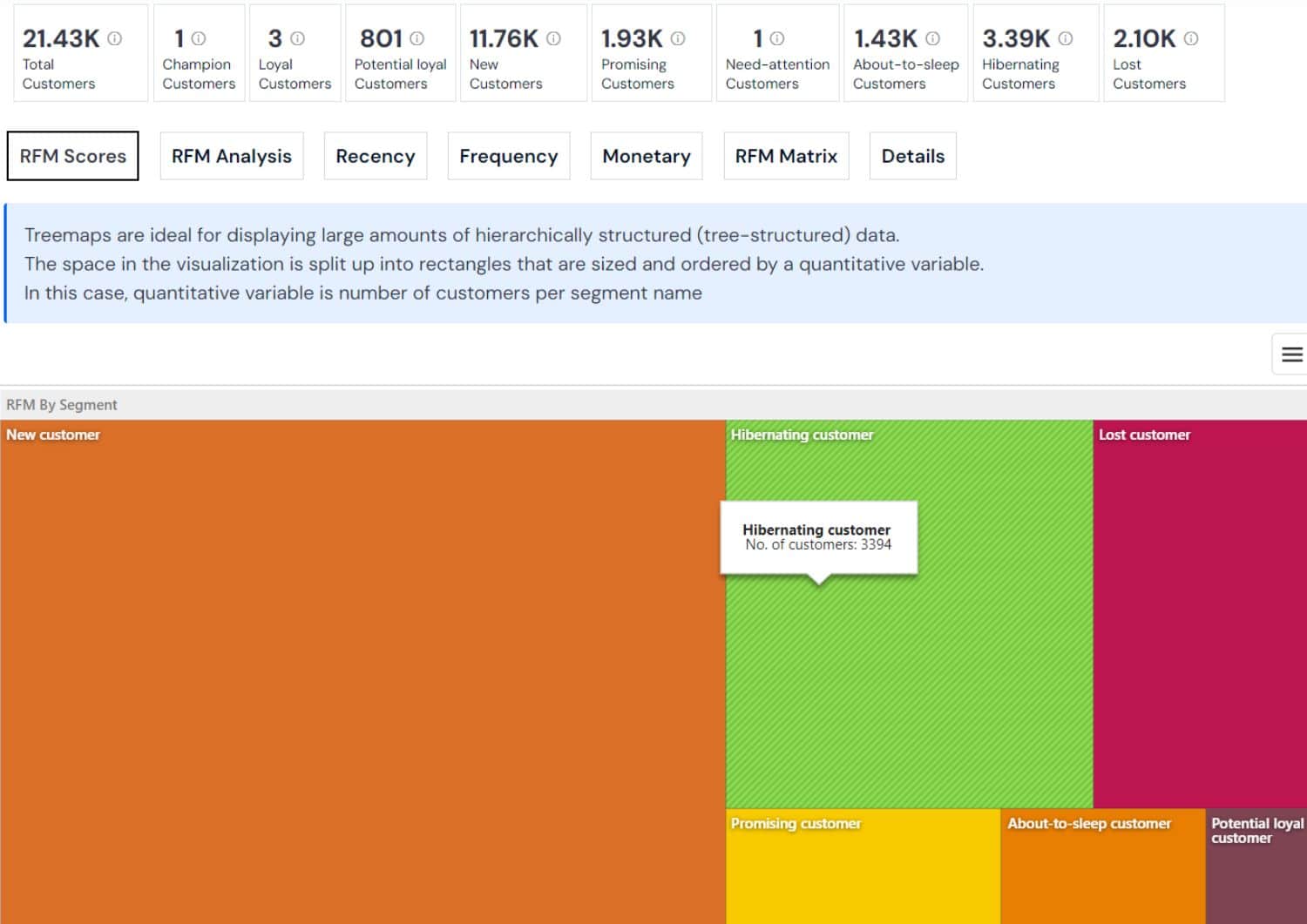
RFM Customer Segmentation: This method analyzes customer value based on three dimensions: Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value. It segments customers into groups to tailor marketing efforts and improve customer engagement strategies.
- Engagement identification: Who are the most recent buyers?
- Loyalty assessment: Who purchases frequently?
- Value analysis: Who spends the most?
- Segmentation for marketing: How to customize communication for each segment?
- Retention focus: Which segments should retention efforts target?
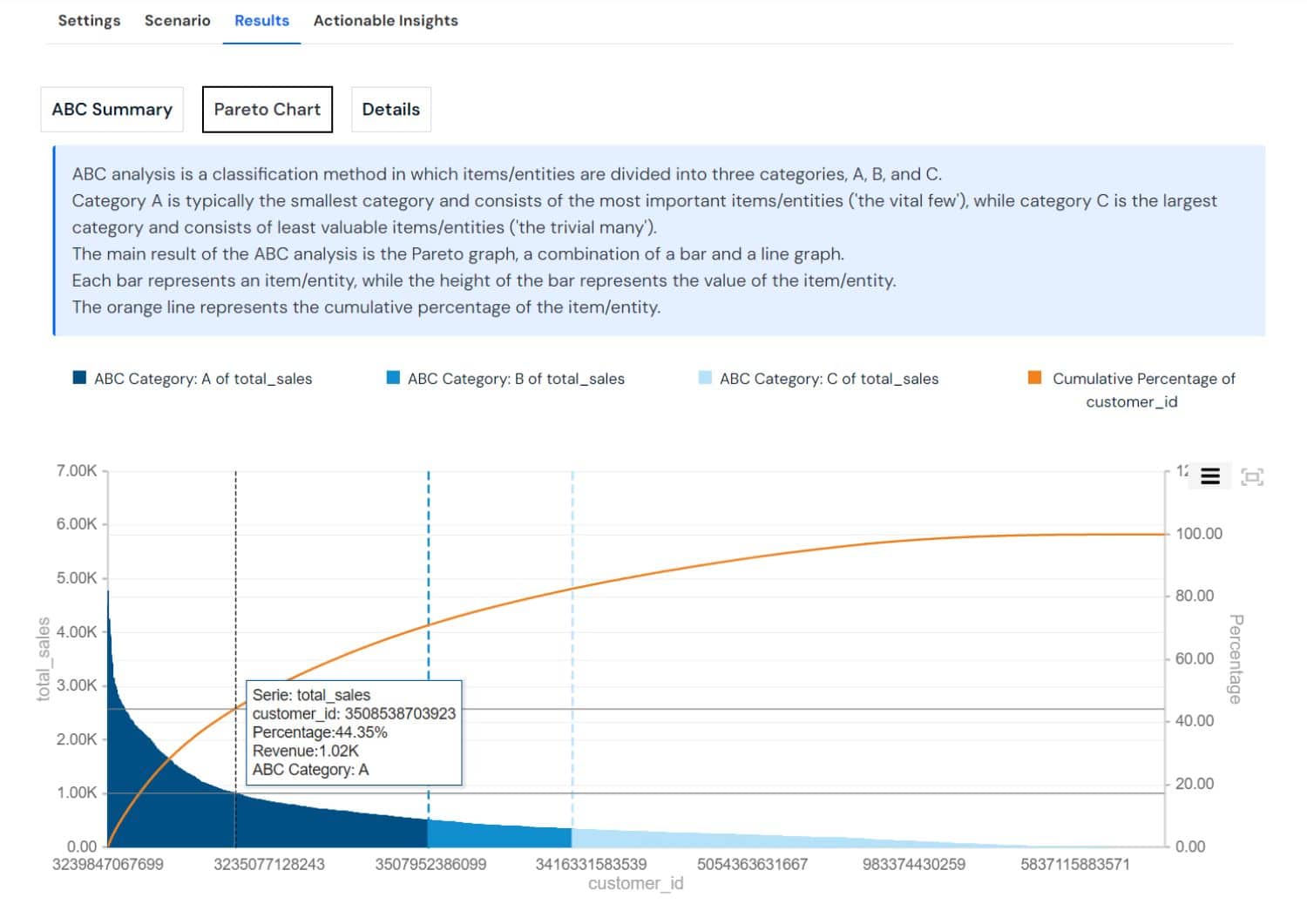
ABC Analysis: This inventory categorization technique divides items into three categories (A, B, and C) based on their importance to the business, helping to prioritize management efforts and resources.
- Priority setting: Which items are critical to business success (A)?
- Efficiency optimization: Which items offer the best balance of cost and value (B)?
- Resource allocation: How to minimize spending on less critical items (C)?
- Stock level management: How to adjust inventory levels for each category?
- Investment focus: Where to allocate resources for maximum impact?
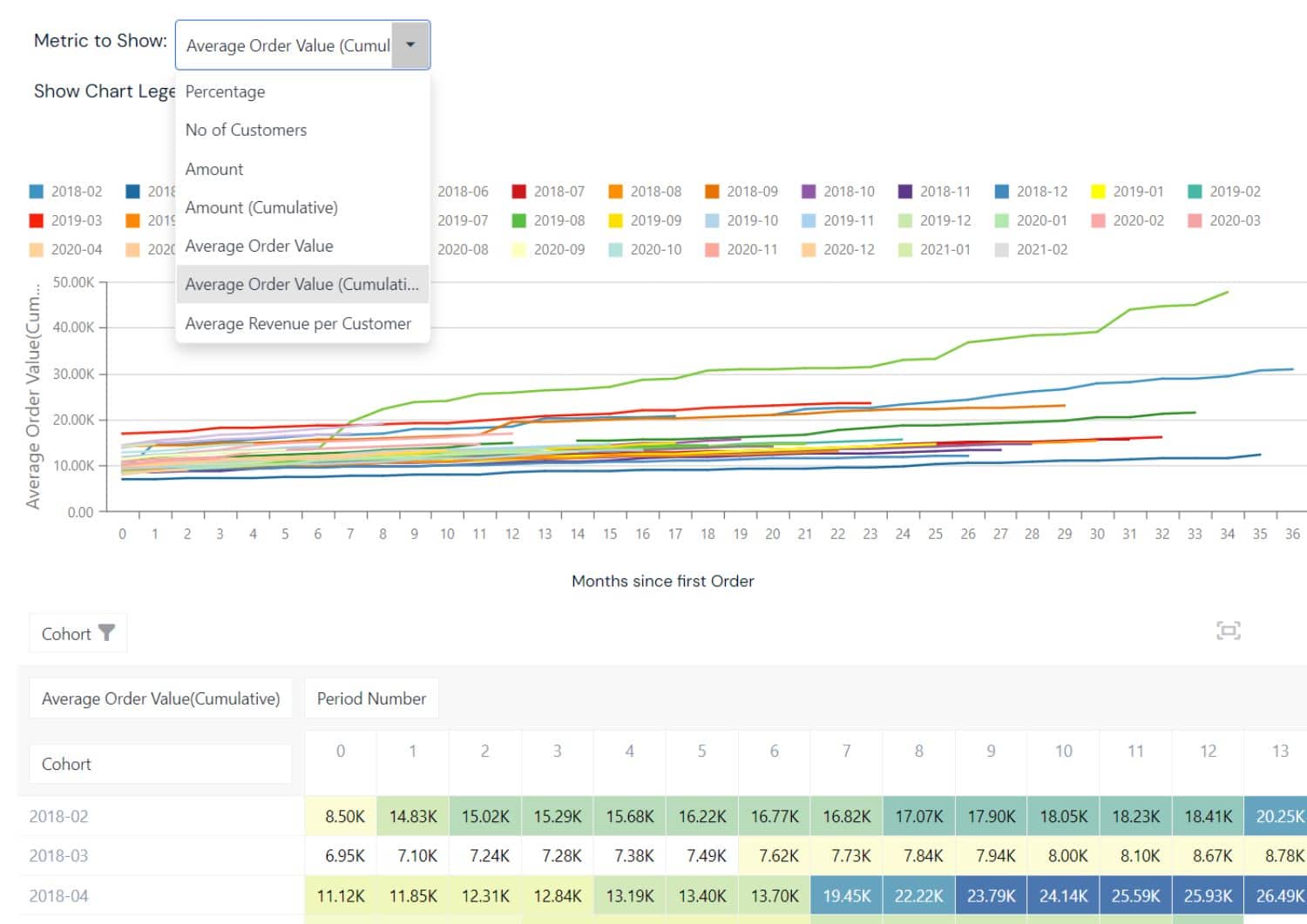
Customer Cohort Analysis: This approach segments customers into cohorts based on shared characteristics or behaviors over time, often focusing on acquisition date. It helps in understanding customer behavior patterns and improving retention strategies.
- Behavior tracking: How do different cohorts behave over time?
- Retention analysis: Which cohorts have the highest retention rates?
- Revenue patterns: How does revenue vary across cohorts?
- Engagement strategies: What strategies work best for each cohort?
- Acquisition optimization: Which acquisition channels bring the most valuable cohorts?
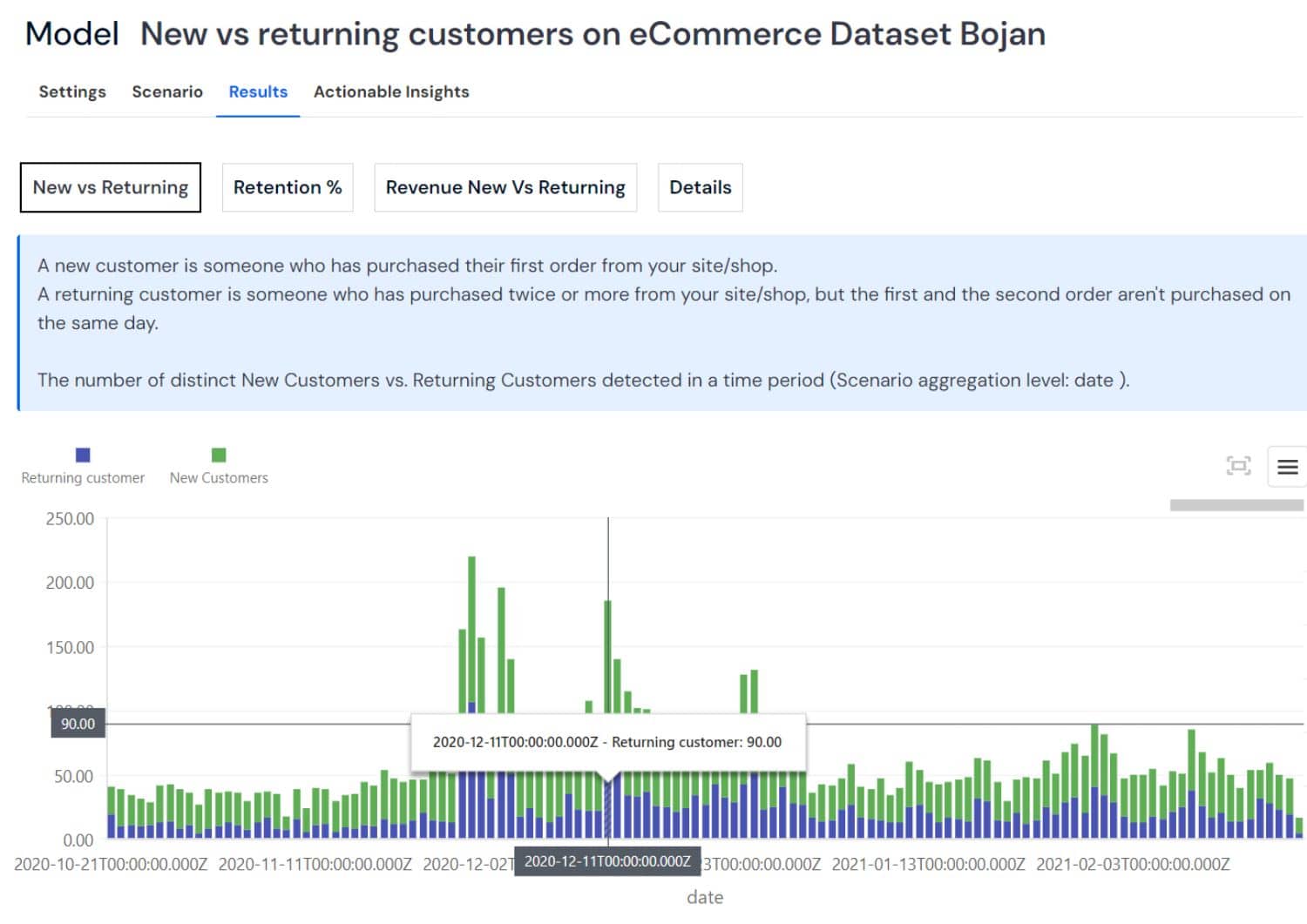
New vs. Returning Customers Analysis: This metric distinguishes between first-time and repeat customers over specific periods, such as weekly or monthly. It's key for understanding customer loyalty and the effectiveness of retention strategies.
- Customer growth: How many new customers are acquired each period?
- Loyalty measurement: What percentage of customers are returning?
- Engagement trends: How does customer engagement differ between new and returning customers?
- Marketing impact: How do acquisition efforts affect new vs. returning customer ratios?
- Retention success: Which strategies are most effective in retaining customers?